Overview
This approach is vital for protecting ICS/OT infrastructures from cyber threats, ensuring system reliability and availability. It is particularly important in environments with legacy equipment, stringent uptime requirements, and strict regulatory compliance standards.
Key Objectives of Industrial Patch Management
Vulnerability Mitigation
Identify and address vulnerabilities in industrial systems to reduce the attack surface.
Operational Continuity
Ensure that patch deployment does not disrupt production or compromise system reliability
Regulatory Compliance
Maintain adherence to industry standards and regulations such as NERC CIP, IEC 62443, and ISO 27001
System Integrity
Prevent unauthorized changes or tampering during the patching process
Risk Reduction
Minimize exposure to known exploits by promptly deploying verified patches
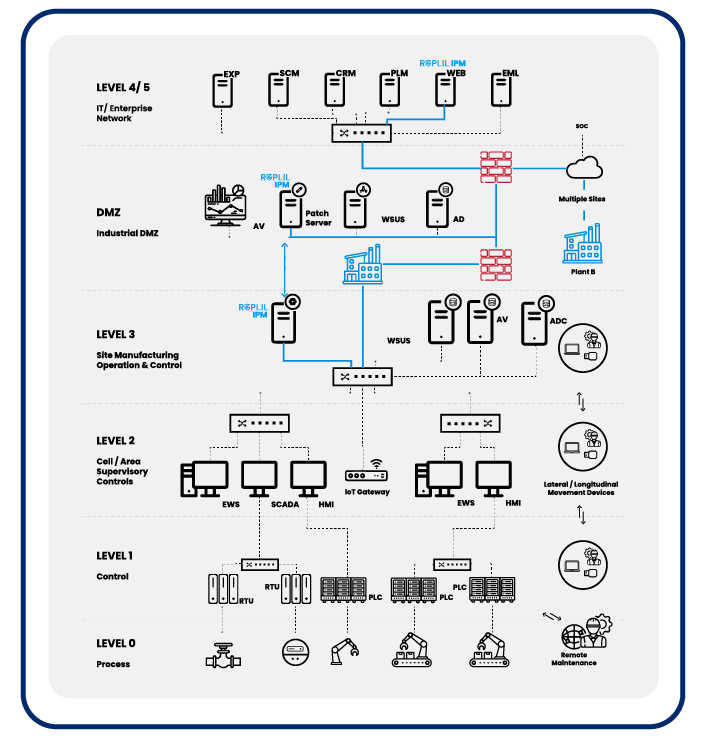
Industrial Patch Management Workflow
- Asset Inventory Creation:
- Identify and document all OT and ICS assets, including software versions and configurations.
- Vulnerability Identification:
- Perform regular scans or leverage threat intelligence feeds to detect vulnerabilities and missing patches.
- Patch Prioritization:
- Rank patches based on:
- Criticality of the asset.
- Severity of the vulnerability (e.g., CVSS score).
- Regulatory requirements.
- Rank patches based on:
- Testing:
- Use a testing environment to evaluate the patch for compatibility, performance, and security implications.
- Scheduled Deployment:
- Apply patches during planned maintenance windows or in a phased manner to minimize disruption.
- Monitoring and Validation:
- Monitor systems post-deployment to ensure the patch has been applied successfully and no issues arise.
- Documentation and Reporting:
- Maintain records of patch activities for audits and regulatory compliance.


Key Benefits of Industrial Patch Management
- Enhanced Security: Protects ICS/OT environments from vulnerabilities, malware, and cyberattacks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Helps organizations meet security standards by maintaining up-to-date systems.
- Operational Reliability: Minimizes downtime and ensures consistent system performance during patching.
- Improved Visibility: Provides a clear understanding of the system’s patch status and security posture.
- Proactive Risk Management: Reduces the likelihood of successful exploits by addressing vulnerabilities promptly.
- Cost Efficiency: Prevents costly breaches or unplanned downtime by maintaining a secure and stable environment.
Use Cases of Industrial Patch Management
- Energy Sector: Ensures that SCADA systems in power grids are updated to protect against attacks on critical infrastructure.
- Manufacturing: Secures industrial robots and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) without disrupting production.
- Oil and Gas: Protects distributed control systems (DCS) from malware and ransomware while maintaining uptime.
- Transportation: Safeguard railway signaling systems and air traffic control networks with timely patching.
- Defense and Government: Ensures that mission-critical OT systems are resilient against emerging cyber threats.

Conclusion
Industrial Patch Management is vital for securing OT and ICS environments, ensuring that vulnerabilities are addressed without compromising system reliability. Organizations can maintain a robust security posture while meeting regulatory compliance by leveraging tools for asset discovery, testing, deployment, and monitoring. This proactive approach to patching is essential for safeguarding critical infrastructure and industrial operations from evolving cyber threats.



